文档对象模型(Document Object Model, DOM)是一种罝于内存中的 JSON 表示方式,以供查询及操作。我们己于 教程 中介绍了 DOM 的基本用法,本节将讲述一些细节及高级用法。
教程中使用了 Value 和 Document 类型。与 std::string 相似,这些类型其实是两个模板类的 typedef:
使用者可以自定义这些模板参数。
Encoding 参数指明在内存中的 JSON String 使用哪种编码。可行的选项有 UTF8、UTF16、UTF32。要注意这 3 个类型其实也是模板类。UTF8<> 等同 UTF8<char>,这代表它使用 char 来存储字符串。更多细节可以参考 编码。
这里是一个例子。假设一个 Windows 应用软件希望查询存储于 JSON 中的本地化字符串。Windows 中含 Unicode 的函数使用 UTF-16(宽字符)编码。无论 JSON 文件使用哪种编码,我们都可以把字符串以 UTF-16 形式存储在内存。
Allocator 定义当 Document/Value 分配或释放内存时使用那个分配类。Document 拥有或引用到一个 Allocator 实例。而为了节省内存,Value 没有这么做。
GenericDocument 的缺省分配器是 MemoryPoolAllocator。此分配器实际上会顺序地分配内存,并且不能逐一释放。当要解析一个 JSON 并生成 DOM,这种分配器是非常合适的。
RapidJSON 还提供另一个分配器 CrtAllocator,当中 CRT 是 C 运行库(C RunTime library)的缩写。此分配器简单地读用标准的 malloc()/realloc()/free()。当我们需要许多增减操作,这种分配器会更为适合。然而这种分配器远远比 MemoryPoolAllocator 低效。
Document 提供几个解析函数。以下的 (1) 是根本的函数,其他都是调用 (1) 的协助函数。
教程 中的例使用 (8) 去正常解析字符串。而 流 的例子使用前 3 个函数。我们将稍后介绍原位(*In situ*) 解析。
parseFlags 是以下位标置的组合:
| 解析位标志 | 意义 |
|---|---|
kParseNoFlags | 没有任何标志。 |
kParseDefaultFlags | 缺省的解析选项。它等于 RAPIDJSON_PARSE_DEFAULT_FLAGS 宏,此宏定义为 kParseNoFlags。 |
kParseInsituFlag | 原位(破坏性)解析。 |
kParseValidateEncodingFlag | 校验 JSON 字符串的编码。 |
kParseIterativeFlag | 迭代式(调用堆栈大小为常数复杂度)解析。 |
kParseStopWhenDoneFlag | 当从流解析了一个完整的 JSON 根节点之后,停止继续处理余下的流。当使用了此标志,解析器便不会产生 kParseErrorDocumentRootNotSingular 错误。可使用本标志去解析同一个流里的多个 JSON。 |
kParseFullPrecisionFlag | 使用完整的精确度去解析数字(较慢)。如不设置此标节,则会使用正常的精确度(较快)。正常精确度会有最多 3 个 ULP 的误差。 |
kParseCommentsFlag | 容许单行 // ... 及多行 /* ... */ 注释(放宽的 JSON 语法)。 |
kParseNumbersAsStringsFlag | 把数字类型解析成字符串。 |
kParseTrailingCommasFlag | 容许在对象和数组结束前含有逗号(放宽的 JSON 语法)。 |
kParseNanAndInfFlag | 容许 NaN、Inf、Infinity、-Inf 及 -Infinity 作为 double 值(放宽的 JSON 语法)。 |
kParseEscapedApostropheFlag | 容许字符串中转义单引号 ‘’` (放宽的 JSON 语法)。 |
由于使用了非类型模板参数,而不是函数参数,C++ 编译器能为个别组合生成代码,以改善性能及减少代码尺寸(当只用单种特化)。缺点是需要在编译期决定标志。
SourceEncoding 参数定义流使用了什么编码。这与 Document 的 Encoding 不相同。细节可参考 转码和校验 一节。
此外 InputStream 是输入流的类型。
当解析过程顺利完成,Document 便会含有解析结果。当过程出现错误,原来的 DOM 会*维持不变*。可使用 bool HasParseError()、ParseErrorCode GetParseError() 及 size_t GetErrorOffset() 获取解析的错误状态。
| 解析错误代号 | 描述 |
|---|---|
kParseErrorNone | 无错误。 |
kParseErrorDocumentEmpty | 文档是空的。 |
kParseErrorDocumentRootNotSingular | 文档的根后面不能有其它值。 |
kParseErrorValueInvalid | 不合法的值。 |
kParseErrorObjectMissName | Object 成员缺少名字。 |
kParseErrorObjectMissColon | Object 成员名字后缺少冒号。 |
kParseErrorObjectMissCommaOrCurlyBracket | Object 成员后缺少逗号或 }。 |
kParseErrorArrayMissCommaOrSquareBracket | Array 元素后缺少逗号或 ] 。 |
kParseErrorStringUnicodeEscapeInvalidHex | String 中的 \\u 转义符后含非十六进位数字。 |
kParseErrorStringUnicodeSurrogateInvalid | String 中的代理对(surrogate pair)不合法。 |
kParseErrorStringEscapeInvalid | String 含非法转义字符。 |
kParseErrorStringMissQuotationMark | String 缺少关闭引号。 |
kParseErrorStringInvalidEncoding | String 含非法编码。 |
kParseErrorNumberTooBig | Number 的值太大,不能存储于 double。 |
kParseErrorNumberMissFraction | Number 缺少了小数部分。 |
kParseErrorNumberMissExponent | Number 缺少了指数。 |
错误的偏移量定义为从流开始至错误处的字符数量。目前 RapidJSON 不记录错误行号。
要取得错误讯息,RapidJSON 在 rapidjson/error/en.h 中提供了英文错误讯息。使用者可以修改它用于其他语言环境,或使用一个自定义的本地化系统。
以下是一个处理错误的例子。
根据 维基百科:
In situ ... is a Latin phrase that translates literally to "on site" or "in position". It means "locally", "on site", "on the premises" or "in place" to describe an event where it takes place, and is used in many different contexts. ... (In computer science) An algorithm is said to be an in situ algorithm, or in-place algorithm, if the extra amount of memory required to execute the algorithm is O(1), that is, does not exceed a constant no matter how large the input. For example, heapsort is an in situ sorting algorithm.
翻译:*In situ*……是一个拉丁文片语,字面上的意思是指「现场」、「在位置」。在许多不同语境中,它描述一个事件发生的位置,意指「本地」、「现场」、「在处所」、「就位」。 …… (在计算机科学中)一个算法若称为原位算法,或在位算法,是指执行该算法所需的额外内存空间是 O(1) 的,换句话说,无论输入大小都只需要常数空间。例如,堆排序是一个原位排序算法。
在正常的解析过程中,对 JSON string 解码并复制至其他缓冲区是一个很大的开销。原位解析(*in situ* parsing)把这些 JSON string 直接解码于它原来存储的地方。由于解码后的 string 长度总是短于或等于原来储存于 JSON 的 string,所以这是可行的。在这个语境下,对 JSON string 进行解码是指处理转义符,如 "\n"、"\u1234" 等,以及在 string 末端加入空终止符号 (‘’\0'`)。
以下的图比较正常及原位解析。JSON string 值包含指向解码后的字符串。
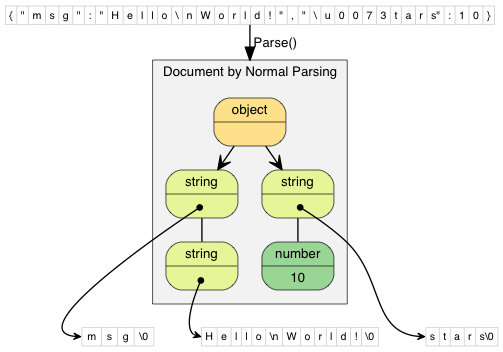
在正常解析中,解码后的字符串被复制至全新分配的缓冲区中。"\\n"(2 个字符)被解码成 "\n"(1 个字符)。"\\u0073"(6 个字符)被解码成 "s"(1 个字符)。
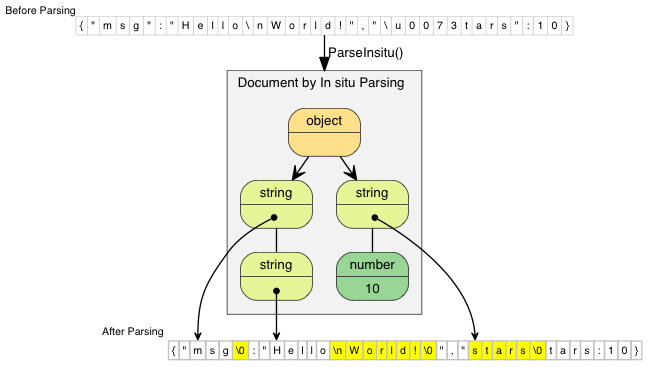
原位解析直接修改了原来的 JSON。图中高亮了被更新的字符。若 JSON string 不含转义符,例如 "msg",那么解析过程仅仅是以空字符代替结束双引号。
由于原位解析修改了输入,其解析 API 需要 char* 而非 const char*。
JSON string 会被打上 const-string 的标志。但它们可能并非真正的「常数」。它的生命周期取决于存储 JSON 的缓冲区。
原位解析把分配开销及内存复制减至最小。通常这样做能改善缓存一致性,而这对现代计算机来说是一个重要的性能因素。
原位解析有以下限制:
原位解析最适合用于短期的、用完即弃的 JSON。实际应用中,这些场合是非常普遍的,例如反序列化 JSON 至 C++ 对象、处理以 JSON 表示的 web 请求等。
RapidJSON 内部支持不同 Unicode 格式(正式的术语是 UCS 变换格式)间的转换。在 DOM 解析时,流的来源编码与 DOM 的编码可以不同。例如,来源流可能含有 UTF-8 的 JSON,而 DOM 则使用 UTF-16 编码。在 EncodedInputStream 一节里有一个例子。
当从 DOM 输出一个 JSON 至输出流之时,也可以使用转码功能。在 EncodedOutputStream 一节里有一个例子。
在转码过程中,会把来源 string 解码成 Unicode 码点,然后把码点编码成目标格式。在解码时,它会校验来源 string 的字节序列是否合法。若遇上非合法序列,解析器会停止并返回 kParseErrorStringInvalidEncoding 错误。
当来源编码与 DOM 的编码相同,解析器缺省地 * 不会 * 校验序列。使用者可开启 kParseValidateEncodingFlag 去强制校验。
这里讨论一些 DOM API 的使用技巧。
在 RapidJSON 中,利用 Writer 把 DOM 生成 JSON 的做法,看来有点奇怪。
实际上,Value::Accept() 是负责发布该值相关的 SAX 事件至处理器的。通过这个设计,Value 及 Writer 解除了偶合。Value 可生成 SAX 事件,而 Writer 则可以处理这些事件。
使用者可以创建自定义的处理器,去把 DOM 转换成其它格式。例如,一个把 DOM 转换成 XML 的处理器。
要知道更多关于 SAX 事件与处理器,可参阅 SAX。
许多应用软件可能需要尽量减少内存分配。
MemoryPoolAllocator 可以帮助这方面,它容许使用者提供一个缓冲区。该缓冲区可能置于程序堆栈,或是一个静态分配的「草稿缓冲区(scratch buffer)」(一个静态/全局的数组),用于储存临时数据。
MemoryPoolAllocator 会先用使用者缓冲区去解决分配请求。当使用者缓冲区用完,就会从基础分配器(缺省为 CrtAllocator)分配一块内存。
以下是使用堆栈内存的例子,第一个分配器用于存储值,第二个用于解析时的临时缓冲。
若解析时分配总量少于 4096+1024 字节时,这段代码不会造成任何堆内存分配(经 new 或 malloc())。
使用者可以通过 MemoryPoolAllocator::Size() 查询当前已分的内存大小。那么使用者可以拟定使用者缓冲区的合适大小。